The ‘Four Cs’ that Determine a Diamond’s Quality and Value
The 4 Cs of diamonds — cut, color, clarity and carat — are the four characteristics that determine a diamond’s quality and value. These are the criteria independent gemological laboratories use to grade diamonds. Today, we want to take you on a small diamond buying guide to determine what the most important purchasing factors are.
What makes a diamond valuable?
Simply put, a diamond’s value is determined by its rarity.
Not all diamonds are created equal. So it’s not just the size of a diamond that determines its price.
When a rough diamond mined from the ground is cut and polished into a gemstone, it becomes truly unique — a one-of-a-kind stone. Although all such cut-and-polished diamonds have value, some have qualities that make them far more rare than most.
The more rare a diamond’s qualities, the more valuable it is.
Professionals called gemologists have a precise methodology to determine a diamond’s rarity and value. This methodology, or grading system, was developed by the Gemological Institute of America in the 1950s. In this grading system, the GIA precisely defines the four characteristics used to objectively evaluate diamonds — what we now know commonly as the four Cs or 4Cs.
Although the GIA defined the 4Cs for the modern era, three of the four Cs have actually been around for over 2,000 years. The very first diamond grading system two millennia ago in India used a diamond’s clarity, color, and carat weight to evaluate a stone’s value.
Learning the four Cs is an essential step as you prepare to buy a diamond. Because every diamond is unique, the four Cs provide an objective standard by which you can compare two or more stones — even if they are at different jewelers.
What are the four Cs of diamonds?
The four Cs of diamonds refer to the diamond’s cut, color, clarity, and carat (weight or size).
The 4Cs of diamonds — taken together — describe the quality of a cut, polished, gemstone-grade diamond. The 4Cs mostly determine the diamond’s value (price).
For example, a diamond with a higher carat-weight is larger, and a larger diamond is more valuable if all other factors are equal. So a 2-carat diamond is more valuable than a 1-carat diamond with similar cut, clarity and color characteristics.
Here’s another example. Colorless diamonds are quite rare; the vast majority of diamonds have a yellow tint to them. A diamond’s yellow hue can range from almost imperceptible to extreme. Therefore, the more colorless a diamond (or the less perceptible a diamond’s yellow tint), the more valuable it is.
Color
Most people think of diamonds as white or clear, but in reality they come in a wide range of colors, from transparent or “colorless” to yellow or brown.
When it comes to white diamonds, the less color a diamond has, the higher the grade and, consequently, the value.
White diamonds are graded on a letter scale, with D, E, and F being the highest “colorless” grades. The closer to Z you get, the more of a yellow tint the diamond will have. If this seems confusing, you can always refer to a diamond color chart for a good visual representation. A diamond color chart will show you everything you need to know about those letter grades as discussed above.
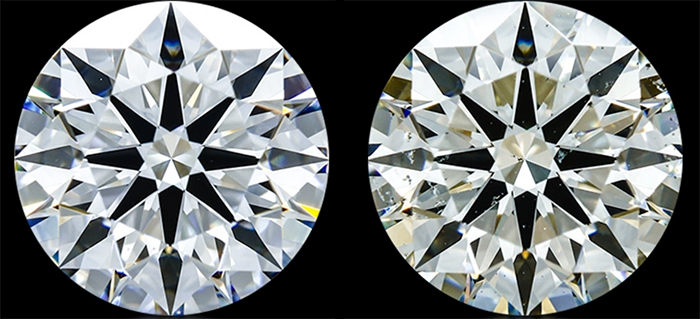
Some other colored diamonds (blue for example) are unique and therefore may be extremely valuable, although these are graded differently.
More: Learn more about diamond color
Clarity
Clarity refers to how clear or “clean” a diamond is.
Diamonds are a natural substance and, as a result, most of them are not perfect. They come out of the ground with imperfections. In the gem world these are called inclusions. Therefore, when you are choosing a diamond to purchase, no matter the diamond shape, you always want to pay attention to grading reports for the source that you are purchasing your diamonds from.
Diamond graders use magnifiers to spot these inclusions and determine how they impact the gem’s appearance. This grade is called diamond clarity, which is one of the leading factors that decides what makes a quality diamond and what falls below the cut.
The fewer inclusions a diamond has, the more valuable it will be. It’s worth noting, however, that many inclusions are not visible to the naked eye.
As far as advice from industry veterans and personal buying advice goes, you can save some money on getting a diamond that has some natural inclusions, as long as they are not visible to the naked eye. If you are having trouble picturing this, referring to a diamond clarity chart is strongly recommended.
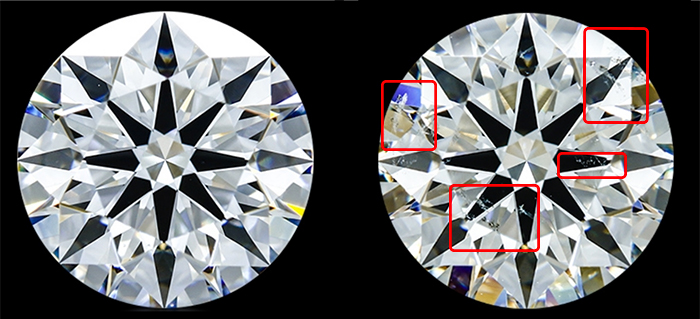
More: Learn more about the diamond clarity grade
Carat
A carat is a unit of mass (weight) used to measure diamonds and other gems. It should not be confused with the homophone karat, which is a unit of a precious metal’s fineness (as in 14-karat gold).
The higher a diamond’s carat-weight, the larger the stone.

Fun fact: The Cullinan Diamond is the largest gem-quality rough diamond ever found. It weighed 3,106 carats (621 grams) when it was mined. The diamond was cut into many gems, but the largest is known as the “Cullinan I” or the “Great Star of Africa”. It weighed 530 carats and is the largest clear cut diamond in the world. The diamond is currently one of the Queen of England’s crown jewels and is valued around £41 million ($54 million).
For comparison, most people buy engagement rings with diamonds sized between less than half of a carat to about two carats.
More: Learn more about diamond carat weight
Cut
A diamond’s cut is arguably the most important of the 4 Cs because it has the biggest impact on the stone’s brilliance (or how much it sparkles).
Although the word “cut” is sometimes used to describe a diamond’s shape — as in, a round- or princess-cut diamond — a diamond’s shape is not one of the four Cs. Rather, cut refers to the diamond’s cut quality.
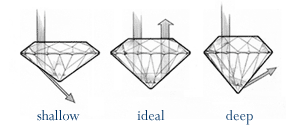
How well a diamond cutter does their job affects how light is reflected through the gem and, as a result, how beautiful and fiery it appears to the human eye. Cut is arguably the most important of the four Cs. A well-cut diamond is a leading factor in determining final diamond quality and how much the stone is going to cost you.
It’s noteworthy, however, that only round- and princess-cut diamonds can be given cut grades. There is not an objective way to measure cut quality on fancy-shaped diamonds such as asscher or heart shapes. Before making any purchase, whether you want a brilliant diamond or otherwise, referring to a diamond cut chart is recommended.
More: Learn more about diamond cut quality
Beyond the 4 Cs
The 4 Cs are the most important characteristics that determine a diamond’s rareness and value. That said, other factors including a diamond’s shape and origin can also affect its value.
Learn more about how to shop for and compared diamonds in our diamond buying guide.